How Much Coal Is Burned to Produce 1 Kwh
Coal facts

Coal is an organically derived material. It is formed from the remains of decayed plant material compacted into a solid through millions of years of chemical changes under pressure and heat. Its rich carbon content gives coal most of its energy content. When coal is burned in the presence of air or oxygen, heat energy is released.
This energy can then be converted to other forms of useful energy. Primary applications for coal are thermal (e.g., electricity generation) and metallurgical (e.g., coking or steelmaking coal).
Key facts
- The main use of coal is electricity generation
- Coal is also a key ingredient in the manufacturing of steel and cement
- Canada's coal production in 2019 was 57 million tonnes
- Canada exported 37 million tonnes of coal and imported 8 million tonnes in 2019
- Canada is the world's fourth largest exporter of metallurgical coal, after Australia, the United States and Russia
- Alberta and British Columbia produced 83% of Canada's coal.
- In 2018, the Government of Canada announced final regulations to phase-out traditional coal-fired electricity by 2030.
Learn more about coal
 Coal industry
Coal industry
In 2017, coal made up 27% of the world's energy supply. In Canada, many parts of the nation have abundant low-cost, domestic coal, while other regions have easy access to an international supply.
The Canadian coal industry produces coal for use in metallurgical applications (e.g., coking or steelmaking) and thermal applications (e.g., electricity generation).
Nearly half of the coal produced in Canada is thermal and half is metallurgical. Some power-generating companies not only use coal for electricity generation but also own coal mines or are involved in coal production themselves. Other companies generate electricity from purchased coal.
 International context
International context
Global coal production in 2019 is estimated at 7.9 billion tonnes, increasing by 116 million tonnes from 2018. The top 5 producing countries accounted for 79% of the world's coal production.
World coal production, 2010–2019 (p)

Text version
This bar chart shows the world's annual coal production from 2010 to 2019. Production in 2010 was 7.2 billion tonnes. It then grew, peaking in 2013 at 7.9 billion tonnes. Production in 2019 was 7.9 billion tonnes.
Find out how Canada's coal ranks on an international scale:
World Production
| Rank | Country | Million tonnes | Percentage of total |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | China | 3,693 | 47% |
| 2 | India | 769 | 10% |
| 3 | United States | 640 | 8% |
| 4 | Indonesia | 616 | 8% |
| 5 | Australia | 503 | 6% |
| 13 | Canada | 57 | 1% |
| - | Other countries | 1,643 | 21% |
| - | Total | 7,921 | 100% |
World exports
| Rank | Country | Million tonnes | Percentage of total |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Indonesia | 455 | 32% |
| 2 | Australia | 393 | 27% |
| 3 | Russia | 217 | 15% |
| 4 | United States | 84 | 6% |
| 5 | South Africa | 81 | 6% |
| 7 | Canada | 36 | 3% |
| - | Other countries | 170 | 12% |
| - | Total | 1,436 | 100% |
World imports
| Rank | Country | Million tonnes | Percentage of total |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | China | 298 | 21% |
| 2 | India | 247 | 17% |
| 3 | Japan | 185 | 13% |
| 4 | South Korea | 130 | 9% |
| 5 | Taiwan | 67 | 5% |
| - | Other countries | 495 | 35% |
| - | Total | 1,424 | 100% |
World proved reserves
| Rank | Country | Million tonnes | Percentage of total |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | United States | 250,219 | 23% |
| 2 | Russia | 162,166 | 15% |
| 3 | Australia | 149,079 | 14% |
| 4 | China | 141,595 | 13% |
| 5 | India | 105,931 | 10% |
| 16 | Canada | 6,582 | 1% |
| - | Other countries | 254,746 | 24% |
| - | Total | 1,069,636 | 100% |
 Trade
Trade
Canada's imports of coal imports have trended downwards for over a decade, while exports have held steady. Canada exports about half of its production. The majority of Canada's coal exports go to Asia, which is still a significant consumer.
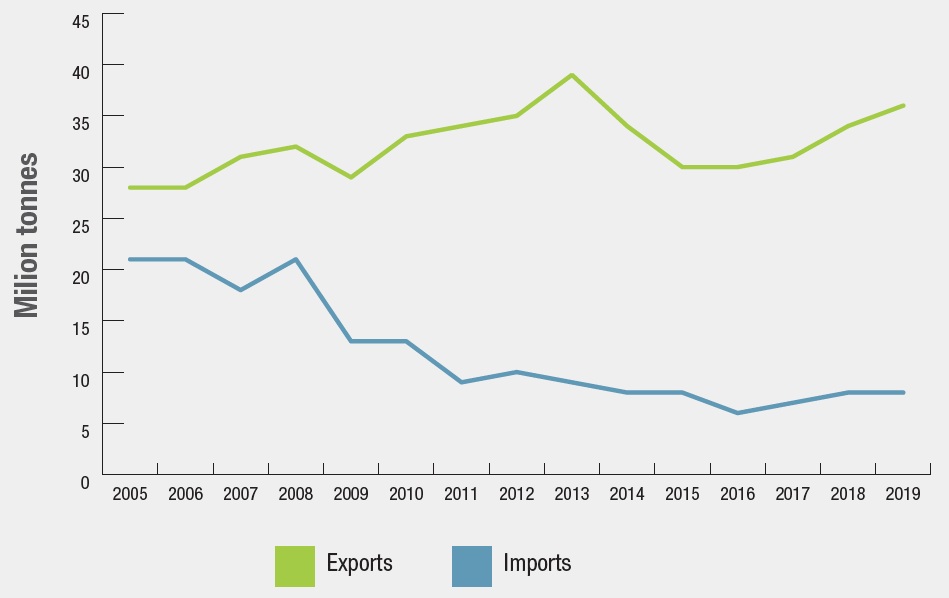
Canadian coal trade, 2005–2019
Text version
From 2005 to 2013, coal exports increased from 28 million tonnes to almost 40 million tonnes before levelling to approximately 30 million tonnes between 2015 and 2017. Coal imports decreased from 21 million tonnes in 2005 to 7.6 million tonnes in 2018.
In 2019, Canada exported 36.5 million tonnes of coal around the world and imported nearly 8 million tonnes of coal, mostly from the United States. Exports to the United States accounted for 2% of Canadian coal exports, and represented 12% of total United States coal imports.
Canada's exports are primarily metallurgical coal (95% in 2019).
Canadian exports and imports of coal (2019)

Text version
In 2019, Canadian exports of coal were valued at 7.1 billion dollars. The major destinations for those exports were South Korea (25%), Japan (23%), India (14%) and China (13%). Approximately two percent of Canada's coal exports are to the United States, representing 12% of U.S. coal imports. As for Canadian coal imports, 73% come from the United States. Nearly half of all imports are used for the manufacturing of steel, the rest is for electricity generation.
 Uses
Uses
Coal is used for electricity generation, the manufacturing of steel and cement, and various industrial and residential applications. Canada produced 57 Mt of coal in 2019, of which 53% is metallurgical coal used for steel manufacturing and 47% thermal coal used for electricity.
In Canada, 7.4% of electricity is generated with coal. Electricity generation consumed 26 Mt in 2018, a 49% decrease from 50.7 Mt in 2008.
With the phasing out of coal-fired electricity by the Government of Canada, energy produced by coal will be eliminated by 2030. That said, coal will continue to be used for metallurgical processes.
Global coal demand by sector, 2019 (p)

Text version
This circular chart shows the major global sources of demand for coal in percentages in 2019. The largest share of coal was used in electricity generation and heating (67%), followed by iron and steel industries (12%), residential, commercial and public services (3%), and other sectors (18%).
 Canadian production
Canadian production
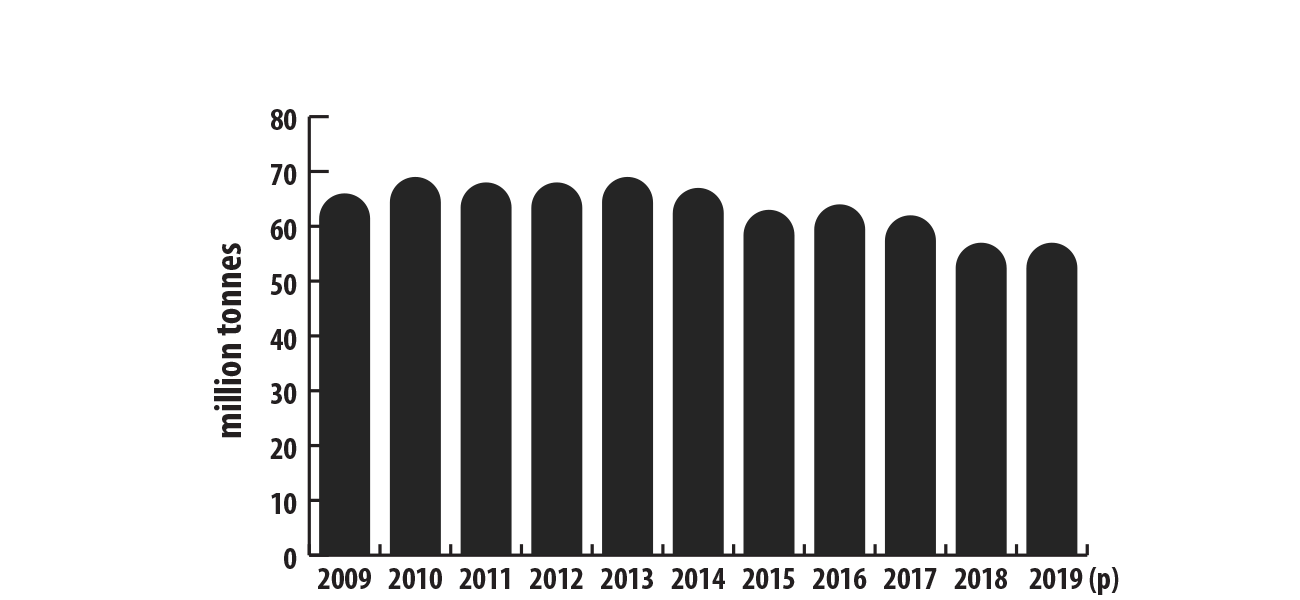
Canadian production of coal has been trending down over the past decade and was 57 million tonnes in 2019.
Canadian coal production, 2009–2019
Text version
This bar chart shows Canada's annual mine production of coal from 2009 to 2019. Production was 66 million tonnes in 2009, followed by some period peaks until 2014, when production began trending downwards. Production in 2019 stayed flat from 2018 at 57 million tons.
Coal production
by province, 2019

Text version
Canada produced 57 megatonnes of coal in 2019. Production by province is as follows: British Columbia 48%, Alberta 35%, Saskatchewan 16%, and Nova Scotia at 1%.
Coal fired generating capacity Footnote * by province, 2019
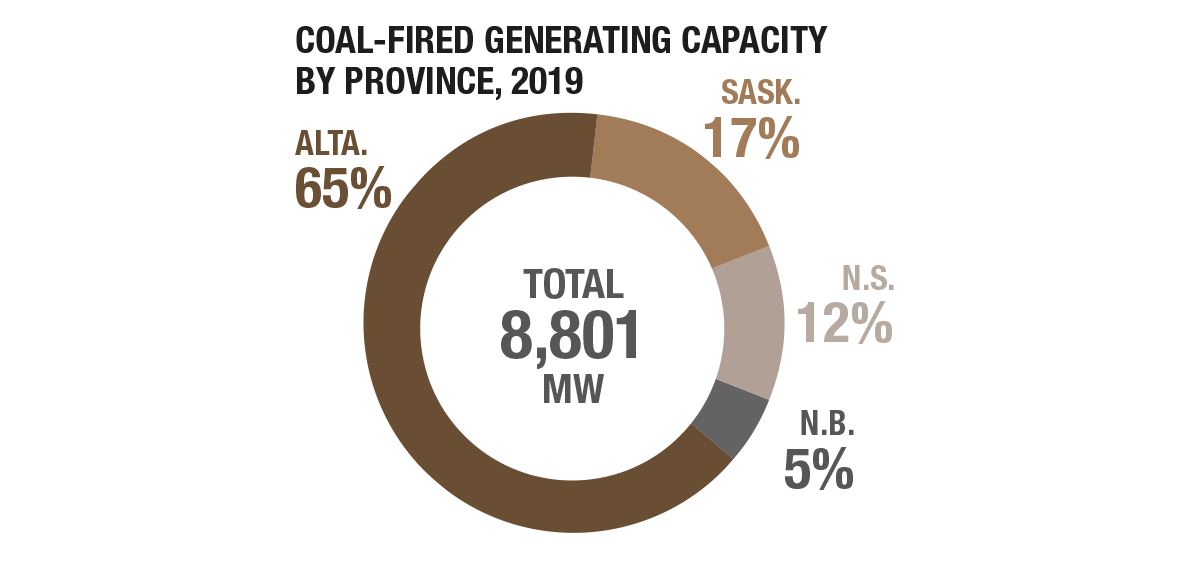
Text version
Canada has a coal-fired electricity generating capacity of 8,801 MW in 2019 (excluding temporarily deactivated capacity). Alberta has the largest proportion of coal-fired generating capacity at 65%, and is followed by Saskatchewan (17%) and Nova Scotia (12%).
Coal used for electricity generation

Text version
Electricity generation consumed 26 Mt in 2018, a 49% decrease from 50.7 Mt in 2008.
 Prices
Prices
After a peak in 2011, global prices for metallurgical coal started on a downward trajectory until the latter part of 2016, when it peaked at US$273 at the end of November. Since then, the prices have been declining, and have levelled at an average of US$175 per tonne in 2019. Globally, thermal coal prices experienced a similar trend.
Australia, Colombia and South Africa are globally recognized as the three terminal markets that determine global thermal coal prices. Coal prices fluctuate with global economic conditions, and recent price increases have occurred in conjunction with temporary mine disruptions in Australia and mine production curtailments in China.
Global coal prices, 2009–2019

Text version
This graph represents the monthly coal prices (USD) from 2009 to 2019
Find out more about minerals and metals facts
- Date modified:
How Much Coal Is Burned to Produce 1 Kwh
Source: https://www.nrcan.gc.ca/science-and-data/data-and-analysis/energy-data-and-analysis/energy-facts/coal-facts/20071
0 Response to "How Much Coal Is Burned to Produce 1 Kwh"
Post a Comment